The Guiana Gnatcatcher: A Closer Look At Polioptila Guianensis
Share
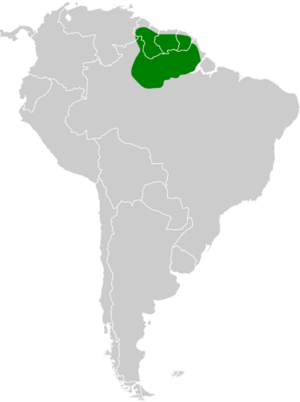
The Guiana Gnatcatcher, scientifically known as Polioptila guianensis, is a fascinating bird species belonging to the order Passeriformes. This small, elusive bird is a member of the family Genera Sedis Incertae and the subfamily Polioptilinae. Found primarily in the lush tropical regions of British Guiana, Surinam, and French Guiana, the Guiana Gnatcatcher is a remarkable example of avian diversity in South America.

Taxonomy and Classification
The Guiana Gnatcatcher was first described by Todd in 1920, with its type locality recorded at Tamanoir, Mana River, French Guiana. It falls under the suborder Oscines, which is known for its songbirds. The classification of this species is as follows:
- Order: Passeriformes
- Family: Genera Sedis Incertae
- Suborder: Oscines
- Subfamily: Polioptilinae
- Species: Polioptila guianensis
- Subspecies: guianensis
Physical Characteristics
The Guiana Gnatcatcher is a small bird, typically measuring around 10 to 12 centimeters in length. It exhibits a slender body with a long tail, which is characteristic of gnatcatchers. The plumage is predominantly grayish-blue, with lighter underparts. The bird's eyes are dark and expressive, contributing to its charming appearance.

Habitat
This species thrives in humid tropical forests, particularly in areas with dense undergrowth. The Guiana Gnatcatcher prefers lowland rainforests, where it can find ample cover and food sources. Its range includes the dense foliage of British Guiana, Surinam, and French Guiana, where it can often be found flitting through the understory.
Diet
The diet of the Guiana Gnatcatcher primarily consists of small insects and arthropods. It forages actively among the foliage, using its agile movements to catch prey. The bird's feeding behavior is characterized by quick hops and short flights, allowing it to navigate through the dense vegetation effectively.

Behavior
The Guiana Gnatcatcher is known for its lively and inquisitive nature. It often forages in pairs or small groups, making it a delightful sight for birdwatchers. The bird's vocalizations are a series of high-pitched calls, which can be heard echoing through the forest. These calls play a crucial role in communication, especially during the breeding season.
Reproduction
Breeding typically occurs during the wet season when food is abundant. The Guiana Gnatcatcher builds a small, cup-shaped nest made of plant fibers and spider silk, usually located in dense vegetation. The female lays a clutch of 2 to 4 eggs, which she incubates for about two weeks. Both parents are involved in feeding the chicks once they hatch, ensuring their survival in the challenging rainforest environment.

Conservation Status
Currently, the Guiana Gnatcatcher is not considered endangered, but its habitat is threatened by deforestation and habitat loss due to agricultural expansion and logging. Conservation efforts are essential to protect the delicate ecosystems where this species resides. Preserving its natural habitat is crucial for maintaining the biodiversity of the region.
Birdwatching Tips
For birdwatchers eager to observe the Guiana Gnatcatcher, visiting the tropical rainforests of British Guiana, Surinam, and French Guiana is highly recommended. Early morning is the best time to spot these birds, as they are most active during this period. Listening for their distinctive calls can also aid in locating them among the dense foliage.
The Guiana Gnatcatcher is a captivating species that highlights the rich avian diversity of South America. Its unique behaviors, habitat preferences, and role in the ecosystem make it a significant bird for both researchers and birdwatchers alike. Observing this charming gnatcatcher in its natural habitat is not only a rewarding experience but also a reminder of the importance of conserving our planet's biodiversity.